Gum health plays a crucial role in overall oral wellness, and emerging research shows that diet and nutrition have a direct impact on the condition of the gums. For patients in Bethesda, MD, understanding how food choices influence oral tissues can help prevent gum disease and promote long-term dental health. At Wyngate Dental of Bethesda, exploring the relationship between nutrition and gum health demonstrates that caring for your gums is not limited to brushing and flossing alone; what you eat can either support or hinder the strength of your gum tissue.
The gums, like other tissues in the body, require essential vitamins, minerals, and nutrients to remain resilient and repair damage. Deficiencies in key nutrients can lead to inflammation, bleeding, and an increased susceptibility to periodontal disease. Conversely, a diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can strengthen the immune response in the oral cavity and protect against bacterial infections. By examining the role of diet in gum health, patients can better understand the importance of holistic care that combines oral hygiene with proper nutrition.
Nutrition also influences oral microbiota, the balance of bacteria in the mouth. Foods high in sugar or refined carbohydrates can encourage the growth of harmful bacteria that contribute to gum disease, while nutrient-dense foods help maintain a healthy microbial environment. For residents of Bethesda, MD, being mindful of dietary choices can be an effective way to complement preventive dental care, supporting the longevity and strength of gums.
Essential Nutrients for Healthy Gums
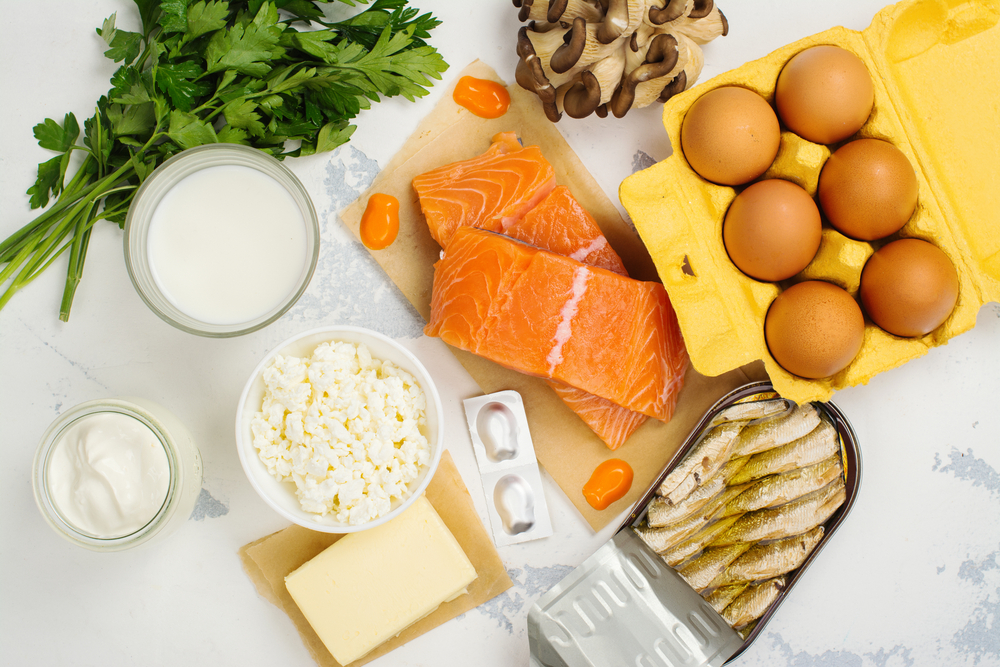
Certain nutrients are particularly critical for maintaining strong, healthy gums. Vitamin C, for example, is vital for collagen production, which provides structural support to gum tissue. A deficiency in vitamin C can lead to weakened gums and a higher risk of developing gingivitis. Foods rich in vitamin C include citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and leafy green vegetables, all of which contribute to gum repair and immune support.
Calcium and vitamin D also play a significant role in oral health. Calcium is necessary for maintaining strong teeth and jawbones, while vitamin D enhances calcium absorption and supports the body’s immune response. Deficiencies in these nutrients can lead to bone loss around the teeth and increased gum vulnerability. Including dairy products, fortified plant-based alternatives, and fatty fish in the diet helps provide these essential nutrients.
Other nutrients that influence gum health include vitamin A, which promotes tissue repair, and antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables, which reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. Zinc and B vitamins also support immune function and tissue regeneration. A well-rounded, nutrient-rich diet creates an environment in which gums can thrive, preventing damage caused by bacterial infection and inflammation.
Dietary Habits That Support Gum Health
In addition to specific nutrients, overall dietary habits influence gum wellness. Minimizing sugary snacks and beverages helps reduce the risk of bacterial overgrowth in the mouth. Frequent consumption of processed foods can also exacerbate inflammation and contribute to periodontal issues. Conversely, incorporating whole foods, fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, and lean proteins supports oral tissue repair and overall gum health.
Hydration is another critical factor in maintaining healthy gums. Drinking sufficient water helps flush food particles and bacteria from the mouth while supporting saliva production. Saliva acts as a natural defense against harmful bacteria, neutralizing acids and maintaining a healthy oral environment. For patients who consume caffeinated or sugary beverages, balancing intake with water helps protect the gums from prolonged exposure to harmful substances.
- Key dietary habits for healthy gums:
- Include vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetables daily
- Consume calcium and vitamin D sources for bone and gum support
- Reduce intake of sugary and processed foods
- Maintain adequate hydration to support saliva and tissue health
- Incorporate antioxidant-rich foods to reduce inflammation
Adopting these habits creates a foundation for gum resilience and complements routine oral hygiene practices, offering long-term benefits to oral health.
The Connection Between Diet, Inflammation, and Gum Disease
Gum disease is largely driven by inflammation caused by bacterial accumulation in the mouth. Diet can influence the severity of this inflammation. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, walnuts, and flaxseed, have anti-inflammatory properties that may reduce the risk and progression of gum disease. On the other hand, diets high in refined carbohydrates and sugar can increase inflammatory responses, exacerbating tissue damage and gum bleeding.
Understanding this connection highlights the importance of preventive care through nutrition. By choosing foods that support immune function and reduce inflammation, patients can mitigate risk factors associated with gum disease. Education about dietary choices reinforces the concept that oral health is part of a broader health ecosystem, where systemic wellness and nutrition intersect with dental care.
For individuals in Bethesda, MD, learning about the role of diet in gum health provides actionable steps that enhance overall oral care. Combining nutrient-rich foods with good oral hygiene can significantly improve outcomes, prevent gum disease, and maintain a healthy, confident smile.
Conclusion
Diet and nutrition are powerful tools in supporting gum health and preventing periodontal disease. By ensuring sufficient intake of vitamins, minerals, and anti-inflammatory foods while minimizing sugar and processed foods, patients can maintain strong, resilient gums. Proper hydration, nutrient-rich foods, and balanced eating habits work together to create an environment that supports tissue repair, reduces inflammation, and promotes overall oral health. Residents of Bethesda, MD, can benefit from understanding how food choices influence gum wellness, emphasizing the interconnectedness of diet, lifestyle, and dental care. Wyngate Dental of Bethesda highlights the significance of integrating nutrition awareness into oral health practices, reinforcing the value of proactive, informed care for lifelong gum health.
Resources
Chapple, I. L. C., & Genco, R. (2013). Diabetes and Periodontal Diseases: Consensus Report of the Joint EFP/AAP Workshop. Journal of Clinical Periodontology.
Wade, W. G. (2013). The Oral Microbiome in Health and Disease. Pharmacological Research.
Woelber, J. P., & Tennert, C. (2016). Nutrition and Periodontal Disease: A Review. Clinical Oral Investigations.